AWS security best practices are essential for protecting cloud workloads from cyber threats, misconfigurations, and unauthorized access. Failing to implement strong security measures can lead to data breaches, compliance violations, and financial loss.
What you'll learn
This guide outlines key AWS security best practices for authentication, auditing, and network security to help organizations reduce risks and strengthen their cloud security posture.
Why AWS Security Matters
AWS operates on a Shared Responsibility Model, meaning that while AWS secures the underlying cloud infrastructure, customers are responsible for securing their workloads, data, and configurations.
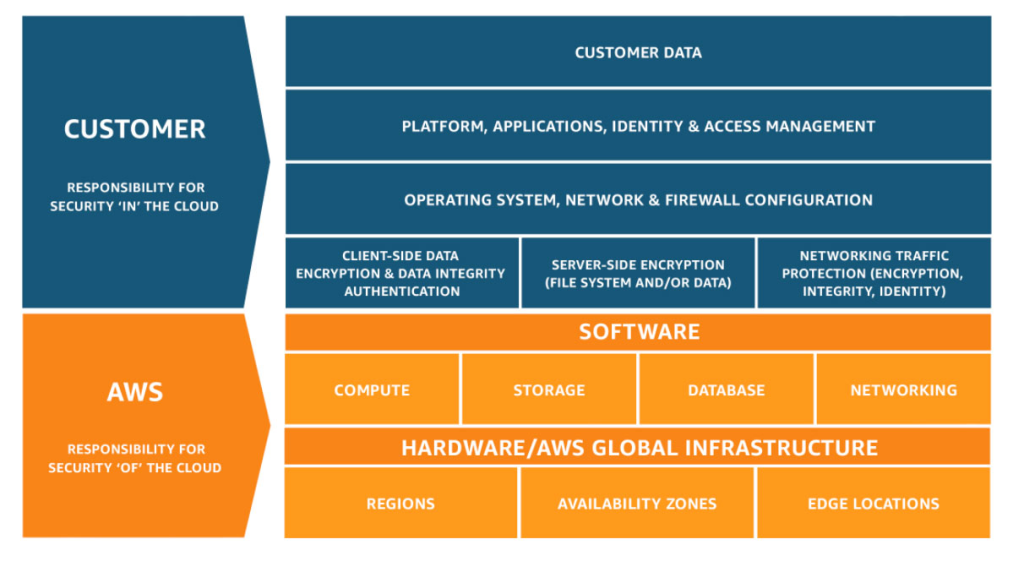
Failing to implement proper AWS security best practices can result in:
-
Data breaches
Misconfigured S3 buckets, weak IAM policies, and unencrypted data can expose sensitive information. -
Unauthorized access
Attackers can gain control of AWS accounts without multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strict IAM roles -
Compliance violations
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and government require strict security compliance (HIPAA, SOC 2, GDPR). -
Financial loss
A compromised AWS account can lead to crypto-jacking, unauthorized resource consumption, and service downtime.
Real-world incidents have shown that even major organizations have suffered data leaks due to misconfigured AWS services.
Key Definition
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model defines who manages what: AWS secures the cloud, while you secure what you put in it (your data, apps, settings).
Essential AWS Security Best Practices
To secure an AWS environment effectively, organizations must focus on three key areas: authentication, auditing, and network security.
Not all security measures carry the same urgency—some are critical and must be implemented immediately, while others enhance security and improve long-term resilience.
Below, we outline the best practices for each area, prioritizing actions based on their impact on security.
Logging in to the AWS Console
Managing authentication and access to the AWS console is a fundamental step in securing cloud workloads. Weak credentials, lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA), and excessive permissions can expose an AWS environment to unauthorized access.
-
Critical: Secure the AWS Root Account
The root account has full access to AWS services and should never be used for daily operations.- Delete root access keys to eliminate credential leaks.
- Do not store the root password in shared documents.
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for root account access.
-
High Priority: Secure IAM Users
Mismanaged IAM permissions are one of the most common security risks in AWS. To mitigate this:- Enforce a strong password policy with complexity requirements.
- Follow the Principle of Least Privilege by granting only necessary permissions.
- Enable MFA for all IAM users, especially administrators and service accounts.
-
Recommended: Use AWS IAM Identity Center (formerly AWS SSO)
For centralized authentication management:- Create users within the IAM Identity Center instead of standalone IAM users.
- Assign roles and policies based on job function.
- Enforce MFA through IAM Identity Center for enhanced security.
-
Nice to have: Federate AWS IAM Identity Center with an Identity Provider (IdP)
Managing IAM users manually can be complex and error-prone. Organizations should:- Connect AWS to an external IdP such as Okta, Google Workspace, or Active Directory.
- Offload password management and MFA enforcement to the IdP to reduce administrative overhead.
Auditing Actions in AWS
Continuous auditing ensures visibility into AWS activities, helping organizations detect misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and security threats. Proper logging and monitoring are essential for compliance and incident response.
-
Critical: Enable AWS CloudTrail for Full Visibility
Without CloudTrail, there is no visibility into user actions, making it difficult to detect security breaches. To ensure full auditing capabilities:- Enable AWS CloudTrail across all AWS regions to log API activity.
- Store CloudTrail logs in encrypted Amazon S3 buckets with restricted IAM access.
- Integrate CloudTrail logs with AWS Security Hub and Amazon GuardDuty for real-time threat detection.
-
High Priority: Secure Log Files to Prevent Tampering
Log integrity is critical for compliance and security investigations. Organizations should:- Encrypt logs stored in S3 using AWS KMS.
- Apply strict IAM policies to restrict who can modify or delete logs.
-
Recommended: Integrate with AWS CloudWatch for Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring helps organizations respond to security threats more effectively. Best practices include:- Setting up CloudWatch alarms for security events, such as failed login attempts.
- Receiving notifications for critical activities via Amazon SNS to enable quick response.
Network Security
Unrestricted network access is a major risk in AWS environments. Implementing segmentation, access control, and secure connectivity reduces the attack surface and minimizes the likelihood of breaches.
-
Critical: Apply the Principle of Least Privilege for Network Access
Network access should follow the same principle of least privilege as IAM policies. Organizations should:- Allow only the minimum necessary network traffic to AWS resources.
- Specify exact IP addresses or CIDR blocks when defining access rules.
-
Nice to have: Restrict Network Access with Security Groups and NACLs
Misconfigured network access settings are one of the most common causes of security incidents. To mitigate risks::- Instead of opening all ports, restrict access to only the necessary ones (e.g., port 22 for SSH).
- Use network ACLs to define explicit allow/deny rules for incoming and outgoing traffic.
-
Recommended: Re-Architect the Network for Security
A well-structured network can prevent lateral movement and unauthorized access. Best practices include:- Creating separate private and public subnets to isolate workloads.
- Placing databases and internal services in private subnets to prevent direct internet exposure.
- Using AWS Systems Manager Session Manager for secure access to private resources instead of opening SSH/RDP ports.
Real-world AWS security enhancements
Implementing AWS security best practices goes beyond compliance. It strengthens data protection, cost efficiency, and system reliability.
Take, for example, the case of Asociația TechSoup, a non-profit organization. After a Well-Architected Framework Review and remediation, they cut down AWS costs by 50% while improving security.
Key security improvements included:
-
Strengthening Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Enforced Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), least privilege access, and AWS IAM Identity Center for better account security. -
Enhancing Network and Threat Protection
Implemented AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF), private subnets, and stricter Security Group rules to reduce exposure. -
Improving Logging and Encryption
Enabled AWS CloudTrail, GuardDuty for real-time monitoring, and AWS KMS encryption to protect sensitive data.
Read the full success story here to find out how the organization eliminated vulnerabilities while optimizing costs.
Conclusion
AWS provides a secure cloud infrastructure, but misconfigurations, weak access controls, and a lack of monitoring remain major risks. Organizations must take an active role in securing their identities, data, and network configurations to prevent unauthorized access and compliance violations.
If you follow a security-first approach, your organization can ensure that AWS workloads remain protected, compliant with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, and resilient against evolving cybersecurity threats.
FAQ about AWS security best practices
Why are logging and auditing important in AWS security?
Logging and auditing help detect unauthorized access, misconfigurations, and security threats. Enabling AWS CloudTrail ensures all API activity is recorded, while storing logs in encrypted Amazon S3 buckets prevents tampering. Additionally, integrating CloudTrail with AWS Security Hub and GuardDuty provides real-time threat detection.
How do I prevent unauthorized access to my AWS account?
Use IAM roles instead of IAM users, restrict access with IAM policies, and regularly review permissions with IAM Access Analyzer. Additionally, set up AWS CloudTrail to monitor login attempts and AWS Security Hub to detect potential threats.
How can I protect my S3 buckets from being publicly accessible?
First, enable S3 Block Public Access, use IAM policies to restrict access, encrypt objects with AWS KMS, and enable S3 Access Logs to track activity. You should regularly audit S3 permissions using AWS Config and AWS Trusted Advisor to ensure no unintended public access is granted.
What is the best way to detect and respond to security threats in AWS?
AWS offers multiple threat detection services: AWS GuardDuty for anomaly detection, AWS Security Hub for centralized security monitoring, AWS CloudTrail for logging API activity, and AWS Config for tracking misconfigurations. To act quickly on detected threats, organizations should set up real-time alerts and automated responses using AWS Lambda and Amazon SNS.
Why is IAM role-based access control (RBAC) better than using IAM users?
IAM roles provide temporary security credentials, reducing the risk of long-term credential exposure. Unlike IAM users, IAM roles follow the principle of least privilege, allowing access only when needed. This approach is more secure, easier to manage, and reduces the likelihood of compromised credentials leading to unauthorized AWS resource access.







